Description
Description
SSD4: Solar energy applications [ARMINES] (specific topic: solar radiation modelling in urban areas, solar energy assessment in different spatiotemporal scales)
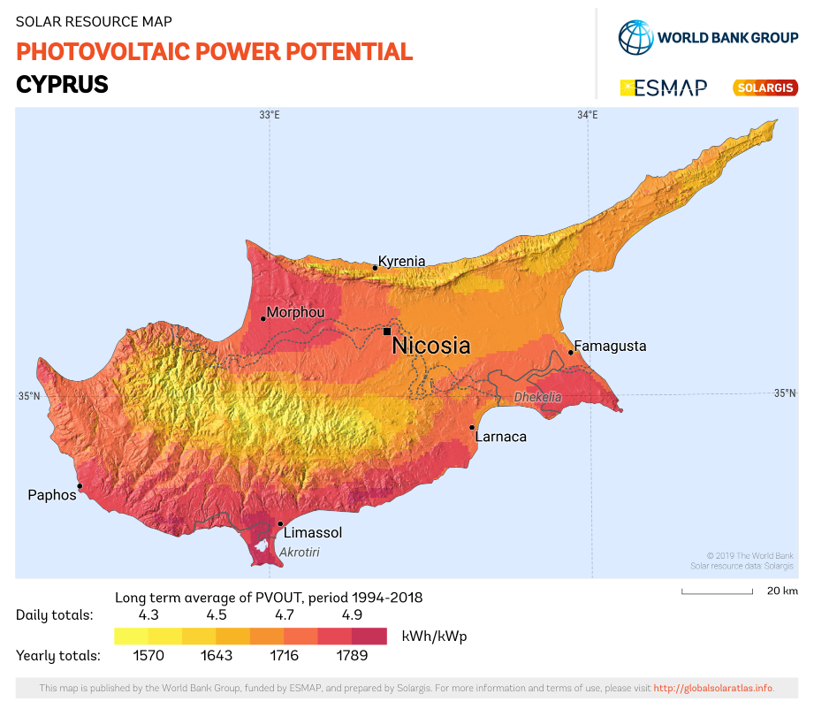
Cyprus is characterised by high year-round insolation (320 sunny days per year); however, it presents a complex and highly variable climatology, in terms of clouds and aerosol patterns that directly affect the incoming solar radiation. This poses a challenge to the modelling and, thus, understanding of the potential, inherent variability, and financials of photovoltaics. One which can only be tackled by a multidisciplinary effort, combining atmospheric sciences, remote sensing and ground-based instrumentation, and engineering.
Therefore, hands-on training will be provided in what concerns the assimilation of complementary sources of information: aerosol data, satellite imagery, ground-based measurements and, particularly for urban contexts, digital surface models – 3D representations of the urban orography. This will involve the modelling of atmospheric attenuation of incoming solar radiation, as well as of the urban shadowing effects and of the PV energy conversion.
Developing competences regarding these data and modelling elements unlocks the capability of developing high-resolution solar cadastre-like products, which are of essence for present and prospective studies, identifying the most suitable urban areas to deploy PV and quantifying the technical potential for regions at given spatial scales to provide renewable electricity. All this is of great interest to various stakeholders, such as the national electricity transmission system operator, public policy makers, private investment funds, as well as researchers and society).