Description
Description
SSD2: Aerosol Microphysics characterization: [GRASP SAS] (specific topic: Inversion modelling for aerosol characterization)
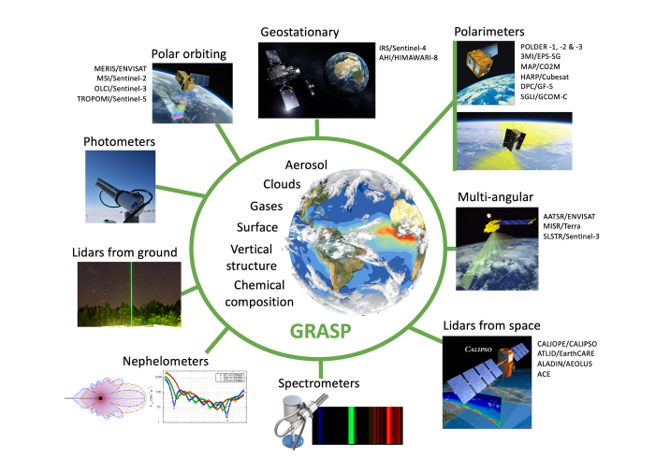
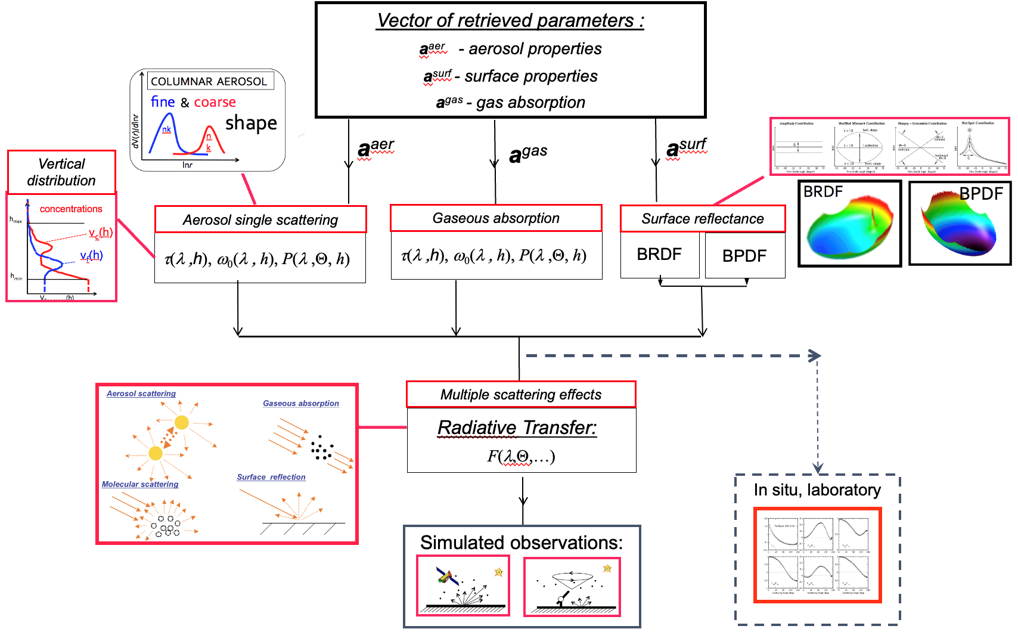
Ground-based passive and active remote sensing can identify and categorize airborne dust particles as well as other aerosol types. For instance, column-integrated aerosol particle properties are provided by passive remote sensing observations with multi-wavelength sun-photometers. Vertical information on the other hand is provided by active systems in form of aerosol backscatter and extinction profiles that are observed with high resolution by multi-wavelength lidar systems. Thus, the observational data required for characterization of aerosol is significantly enhanced and extended by the combination of sun-photometers and lidar observations. To achieve this, retrieval methods have been developed that take advantage of co-located active and passive remote sensing measurements. The starting point for advancing ECoE’s capacity will be the integration of ground-based monitoring capabilities, together with existing space-based observational infrastructures to the Generalized Retrieval of Atmosphere and Part B – Page 7 of 33 Surface Properties (GRASP) algorithm. The state-of-the-art GRASP algorithm, built on the heritage of the well established AERONET retrieval, derives both vertically resolved and columnar information about aerosol particles. The ATARI training scheme will focus on the capacity building of ECoE team on the application of GRASP for the characterization of dust particles and their diurnal cycles as well as aerosol mixtures, e.g., for dust and smoke and for dust and marine particles that often influence Easter Mediterranean. GRASP SAS team is expected to assist greatly in theoretical and practical knowledge transfer required to achieve these goals.